Author: Baily Ramsey
According to UNEP, roughly 30% of the food produced worldwide is lost or wasted every year, contributing to severe environmental, economic, and social consequences. To minimize its effects, innovative waste management solutions are being increasingly adopted by countries around the world to divert food waste from landfills and achieve sustainability goals.
Thanks to advances in food waste technology, anaerobic digestion has emerged as a valuable approach in sustainability efforts, gaining widespread attention for its ability to convert organic waste into renewable energy and nutrient-rich fertilizer. Let’s explore the benefits of converting food waste through anaerobic digestion, understand how the process works, and discover how renewable energy technologies are being leveraged in India.
What is Anaerobic Digestion?
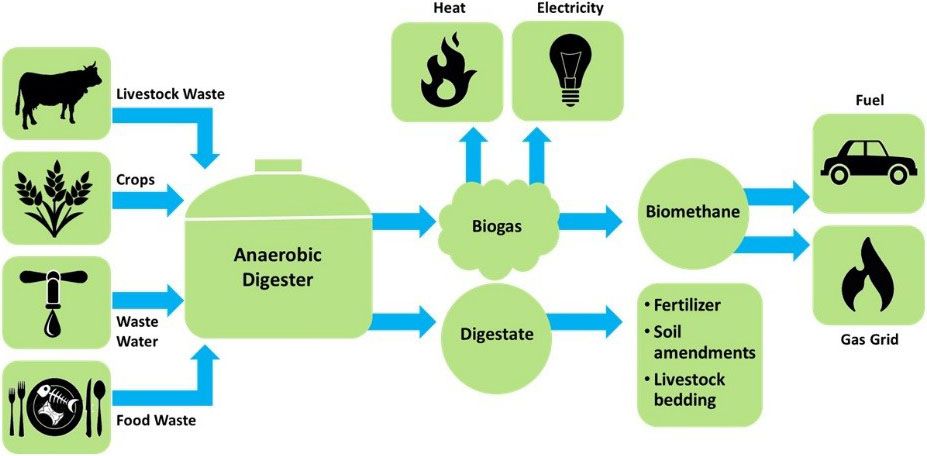
Anaerobic digestion is a series of biological processes in which microorganisms break down organic matter in the absence of oxygen. This process results in two valuable outputs: biogas, a renewable energy source, and digestate, a useful by-product that can be used in multiple agricultural applications.

Benefits of Anaerobic Digestion
There are numerous benefits in converting food waste through anaerobic digestion, which can contribute to environmental initiatives around the world:
Landfill Diversion
There are many long-term benefits of diverting food from landfills, such as minimizing the need for additional landfill space, reducing soil contamination, and decreasing water pollution. Since anaerobic digestion can divert food waste from commercial and household settings, along with fats, oils, grease, and yard waste, it reduces the chances of water pollution as well.
Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions
When food waste decomposes in landfills, it produces methane, a powerful greenhouse gas (GHG) that contributes to global warming. In total, global food loss and waste generate about 8% of total anthropogenic GHG emissions, showcasing its growing impact on environmental issues. In addition to diverting food waste from landfills, anaerobic digestion systems help address this issue by capturing methane, allowing companies to use it beneficially.
Renewable Energy Generation
One of the biggest benefits of anaerobic digestion is its ability to transform food waste into an eco-friendly, renewable energy source. Biogas, which consists of both methane and carbon dioxide, is a cost-effective solution that can be used for various applications, including electricity, heating, and transportation fuel.
Enhances Soil Health
Digestate is a nutrient-rich residue that can be used as fertilizer to improve soil health, making it a valuable resource for the agricultural sector. In addition to improving plant growth and reducing soil erosion, digestate eliminates the need for chemical fertilizers, making it an eco-friendly approach that reduces pollution.
Process of Anaerobic Digestion

So how does this process work? While anaerobic digestion does occur naturally in regions such as marshes and wetlands, it can be mimicked in controlled settings to address large-scale waste. This process consists of four main steps:
- Hydrolysis: During this initial stage, bacteria break down organic materials such as carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids into smaller compounds like sugars, amino acids, and fatty acids. This allows the next group of bacteria to further process the decayed
- Acidogenesis: This is the fermentation stage where the output of hydrolysis are broken down by acidogenic bacteria to produce alcohols, aldehydes, and volatile fatty acids.
- Acetogenesis: During the third stage, acetogenic bacteria further break down the products generated during acidogenesis into acetic acid, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide, maintaining the anaerobic environment necessary for the process.
- Methanogenesis: This is the final stage of anaerobic digestion, where microorganisms convert acetic acid, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide into methane and carbon dioxide. As a result, food waste that would otherwise be sent to landfills is transformed into biogas and digestate, which both have numerous environmental benefits.
Potential of Renewable Energy Technologies in India
India is today recognized as a strong supporter of sustainable power. A study conducted to evaluate the various opportunities and challenges in anaerobic digestion, highlighted its potential to accelerate socio-economic growth. The study revealed that biomass currently accounts for nearly 75% of the overall energy use in rural India, with more than 70% of the rural population depending on it. It is believed that anaerobic digestion can increase these efforts by helping achieve off-grid energy demands for decentralized production of power for lighting, water pumping, dairy production, and other agro-allied industries.
Overall, anaerobic digestion technology can help India address the current indoor air pollution problem due to firewood usage and meet the United Nations’ objective of ensuring access to affordable, reliable, and sustainable energy for all by 2030. While this study focuses specifically on India, it shows the increasing relevance of food waste technology and solutions like anaerobic digestion in combating food waste and generating renewable energy.
Final Thoughts
As technology continues to evolve, advanced food waste management becomes even more attainable, providing us with innovative solutions that address large-scale waste. Over time, we expect to see more widespread adoption of these practices, therefore increasing the production of renewable energy and nutrient-rich fertilizer and helping businesses and governments achieve sustainability goals. By getting everyone involved, we can create a zero-waste future.
Source link
ecoideaz www.ecoideaz.com