1. Introduction
Although these studies have mainly examined specific cases without allowing easy generalization, or have developed indices to evaluate the credibility of specific central banks, they represent a crucial step in understanding this essential aspect of economic policy. While the development of these indices has allowed researchers to more precisely explore the effects of credibility on exchange rate volatility and even suggest an optimal level of credibility, it should be noted that all these indices are based on the assumption that the availability of more abundant or more precise information automatically leads to greater transparency, without considering potential frictions related to how information is communicated.
2. Conceptualization and Theoretical Background
2.1. Central Bank Credibility
The issue of central bank credibility sparks lively debate in both the public and academic spheres regarding monetary policy. Citizens demand more credibility to ensure accountability from central banks, which enjoy increasing independence.
Concurrently, a growing body of research examines the economic implications of greater transparency in monetary policy.
2.2. Exchange Rate Volatility
2.3. Central Bank Credibility and Exchange Rate Volatility
2.4. Previous Bibliometric Studies on Central Bank Credibility and Exchange Rate Volatility
3. Methodology
Biblioshiny was utilized for performance analysis, focusing on evaluating various metrics inherent to the academic field. This assessment encompassed research article quantities, reference occurrences, and collaboration trends to gauge the effect and sway of the analyzed papers. For instance, a topic chart, typically generated utilizing Bibliometrix, visually represented the thematic structure within a collection of scholarly works.
Moreover, it highlighted clusters of related topics, emphasizing central themes and their interrelationships. In network visualization, VOS viewer was employed to create visual representations capturing the intricate relationships and collaborations among various entities within the scholarly domain. This tool facilitated the identification of clusters, trends, and significant connections, thus offering a comprehensive understanding of the structure and dynamics of the scholarly landscape.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Data Description
4.2. Performance Analysis Published
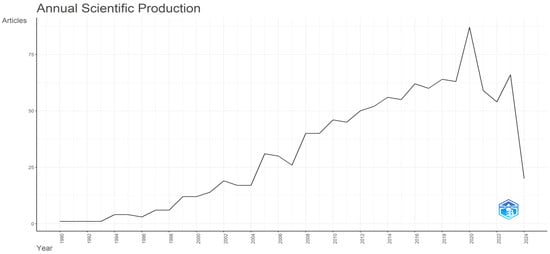
4.2.1. Document Evolution
4.2.2. Source’s Impact
H-index: a measurement that indicates the impact of a journal’s publications based on the number of citations received by its articles.
TCs: the total number of citations received by the journal’s articles.
NPs: the number of published papers.
PY start: the year in which the journal’s publication started.
4.2.3. Authors Impact
4.2.4. Most Locally Cited Documents
This study examined inflation targeting, which essentially involves targeting inflation forecasts: the central bank’s inflation forecasts then become a clear interim goal. Targeting rising prices forecasts streamlines both implementing and monitoring monetary policy. Balancing the weighting of results decides how rapidly inflation forecasts are adjusted towards the inflation target. Compared to inflation targeting, targeting money growth or exchange rates is generally less effective and leads to greater inflation variability. Commitment to “targeting rules” may be preferable to commitment to “instrument rules”.
This document analyzes the implementation of inflation targeting in a small open economy, taking into account both total supply and demand with a microeconomic basis, as well as practical stylized delays in the various channels of the transmission of monetary policy. It also compares strict and flexible targeting of CPI and domestic inflation, as well as reactions to inflation targeting and the Taylor rule. Flexible CPI inflation targeting affects not only the variability in CPI inflation but also that of the output gap and the real exchange rate. Negative productivity supply shocks and positive demand shocks have similar effects on inflation and the output gap, leading to similar monetary policy responses.
This paper uses a principal–agent framework to determine how a central banker’s incentives should be structured to promote an optimal policy on a societal level. Unlike previous findings based on ad hoc targeting rules, the inflationary bias of discretionary policy is eliminated, and an optimal response to shocks is achieved through an optimal incentive contract, even when a central bank has private information. In the one-period model, which has been the basis for much of the literature on discretionary monetary policy, it is demonstrated that the optimal contract ties the rewards of a central banker to realized inflation.
This article examines how changes in monetary policy affect stock prices, with the aim of measuring the average reaction of the stock market and understanding the economic reasons behind this reaction. It is observed that, on average, a hypothetical unanticipated 25-basis-point decrease in the federal funds rate target is associated with about a 1% increase in broad stock indexes. Using a methodology developed by Campbell and Ammer, it was found that the effects of unanticipated monetary actions on expected excess returns account for the largest part of the stock price reaction.
This article seeks to determine whether there is information asymmetry between the Federal Reserve and the public by analyzing the inflation forecasts of the Federal Reserve compared to those of commercial forecasters. It highlights that the Federal Reserve possesses significant information about inflation beyond what is available to commercial forecasters. Additionally, it demonstrates that monetary policy actions send signals about the information held by the Federal Reserve, leading commercial forecasters to adjust their forecasts accordingly. These findings can help understand why long-term interest rates tend to increase in response to tighter monetary policies.
The research examines models of the separation or combination of banking regulation and monetary policy functions in different countries. It emphasizes that no model clearly has the advantage, with arguments in favor of each approach. The question of regulatory design depends on the financial structure of each country. The article argues that combining functions can help prevent systemic crises, but central banks are moving away from this primary role due to structural changes in the banking system. Regulation tends to shift under the control of independent bodies, although central banks continue to play a crucial role as a source of last-resort liquidity.
4.2.5. Conceptual Structure
The authors’ keyword cloud highlights that the core subject tackled by the bulk of scholars is monetary policy and then inflation targeting, which ranks second in sequence in the articles. Additionally, the Taylor rule and banking supervision are closely linked to central bank credibility and exchange rate volatility.
The niche themes concern the ECB, coexisting with responses. The next grouping deals with the theme of governance, and is linked with power.
5. Conclusions
Through this review, we conducted a comprehensive bibliometric and scientometric analysis focusing on research on central bank credibility and exchange rate volatility. This analysis allowed us to highlight key trends and the structure of knowledge, both intellectually and conceptually. This survey analysis enriches the prevalent understanding by shedding light on the growing improvements in academic inquiry at the convergence of central bank transparency and exchange rate volatility. We identified the most productive institutions and individuals in this field, as well as the most cited studies. Additionally, we are able too btain a brief over view of the core problems in this field, which could guide researchers interested in this intersection. We examined the emergence of central bank credibility and exchange rate volatility, as well as the impact of monetary policy transparency and inflation targeting as fundamental issues in the context of central bank credibility. As a result, we have proposed various theoretical and functional outcomes, particularly regarding the constraints of this subject area, thus identifying prospective paths of anticipated inquiry programs.
6. Implications
However, bibliometric abstracts and comprehensive assessments of literature on central bank credibility and exchange rate volatility have received little attention. Thus, through the analysis of 1124 academic research articles combining the concepts of central bank transparency and exchange rate volatility, this article contributes to the literature by dynamically mapping central bank credibility and exchange rate volatility and applying a bibliometric study;that is to say, this study has enriched the understanding of the present corpus by accentuating the growing progressions in scientific research on central bank transparency and exchange rate volatility. In doing so, we identified the main sources of publication, reference networks, leading studies, and the highly prolific scholars in this area, thus summarizing the main topics of discussion that can serve as a pathway for upcoming inquiries on central bank credibility and exchange rate volatility. To understand the interval linking central bank transparency and exchange rate volatility, research must analyze multiple inter-graded investigations and intentionally distinguish the channels of central bank credibility transmission to influence exchange rate volatility. Concerning this issue, the key elements associated with central bank credibility and exchange rate volatility have been emphasized: transparency of monetary policy, inflation targeting, and governance.
Moreover, this bibliometric review of the literature on central bank credibility and exchange rate volatility offers several practical implications for policymakers and central bank governors. Governors should leverage the benefits of transparency, particularly by harnessing commercial interactions supported by information and communication technologies.
7. Research Limitations and Future Directions
This research review, despite its significant contributions both theoretically and practically, has certain limitations, as is often the case in research studies;.however, these limitations also pave the way for significant opportunities to guide future research. For example, while this article relied on documents from the WoS and Scopus databases, it would be beneficial for future studies to consider other sources, such as Science Direct, Google Scholar, IEEE Xplore, or PubMed. This would provide a more comprehensive perspective and additional information on the current research theme. Additionally, this study was limited to documents in English, whereas the inclusion of publications in other languages could enrich our understanding of the field. Future research could also deepen the findings of this study by examining the study approaches and statistical methods used in the field of central bank credibility and exchange rate volatility. Furthermore, it is essential for future studies to adopt effective research methods and rigorous analysis procedures, tailored to the diversity of disciplines and contexts in the field of central bank credibility and exchange rate volatility.
7.1. Cluster 1: Monetary Policy and Independence
A prospective analysis is recommended to explore several key areas related to the intersection of central banking and supervisory responsibilities. First, it is important to investigate how the loss of bank supervisory responsibilities by central banks might impact the conduct and effectiveness of monetary policy. Furthermore, analyzing how confidential bank supervisory information enhances the accuracy of macroeconomic forecasting by central bank staff, and how it influences monetary policy decisions, is crucial. Additionally, examining the extent to which members of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) utilize this confidential information in shaping monetary policy, and the implications for policy effectiveness, should be a focus. The analysis should also assess the complementarity between bank supervisory duties and monetary policy in achieving central bank objectives, exploring the potential consequences for the central bank’s organizational structure. Finally, potential reforms or adjustments to central bank structures should be explored to better integrate supervisory responsibilities with monetary policy mandates, ultimately aiming for improved policy outcomes.
7.2. Cluster 2: Monetary Policy and Exchange Rate Framework
A predictive evaluation is advised to delve into several critical aspects of inflation targeting in small open economies, particularly those with forward-looking aggregate supply and demand. First, it should further examine the implications of inflation targeting while considering additional factors like exchange rate dynamics, international trade, and capital flows. Furthermore, investigating the effectiveness of various inflation-targeting strategies such as strict versus flexible targeting of different inflation measures, including the Consumer Price Index (CPI) and domestic inflation, is essential for understanding their roles in achieving macroeconomic stability and promoting economic growth. The analysis should also explore the optimal design of inflation-targeting reaction functions and Taylor rules in response to different economic shocks, weighing the trade-offs between stabilizing inflation, addressing the output gap, and maintaining exchange rate stability. Additionally, it is important to assess the transmission channels of monetary policy in these economies, particularly the roles of financial intermediaries, asset prices, and expectations formation in influencing inflation and output dynamics. Finally, the analysis should examine the implications of asymmetric shocks, such as negative productivity supply shocks and positive demand shocks, on inflation dynamics and output fluctuations, evaluating how effectively monetary policy responses can mitigate the adverse effects of these shocks.
7.3. Cluster 3: Monopolistic Competition andMonetary Policy
Future studies are recommended to investigate several crucial aspects related to the zero lower bound on nominal interest rates and their implications for monetary policy effectiveness and macroeconomic stability, especially in contexts where average inflation is very low. Researchers should examine how various monetary policy feedback rules such as interest rate targeting versus inflation targeting affect the severity of real distortions that arise from the zero lower bound. Additionally, it is important to explore the role of price-setting behavior in shaping the impact of the zero lower bound on the real economy, taking into account factors like forward-looking versus backward-looking price-setting mechanisms and the degree of price level persistence. Assessing the effectiveness of alternative policy measures, including unconventional monetary policies (such as forward guidance and quantitative easing) and fiscal policy interventions, will also be essential in mitigating the adverse effects of the zero lower bound on economic activity and inflation dynamics. Finally, future studies should investigate the interactions between monetary policy, price-setting behavior, and macroeconomic outcomes in various economic environments, including periods characterized by low inflation, deflationary pressures, or economic downturns.
7.4. Cluster 4: Monetary Policy and Models
Prospective analyses are suggested to further investigate the implications of the zero lower bound on the effectiveness of monetary policy and the efficacy of fiscal policy, emphasizing the importance of considering the entire path of expected future short-term interest rates rather than just the current rate. Additionally, it is essential to examine how different measures of the zero lower bound’s effects on yields of various maturities can provide insights into the transmission mechanisms of monetary and fiscal policies across different time horizons. Researchers should explore the factors driving the dynamics of longer-term yields during periods of near-zero short-term interest rates, including the roles of market expectations, risk premia, and unconventional monetary policy measures. Furthermore, assessing the timing and magnitude of the transition from relatively unconstrained longer-term yields to more constrained yields will be crucial in understanding the implications for the effectiveness of monetary and fiscal policies in stimulating economic activity and achieving price stability. Finally, it is important to investigate how variations in the degree of yield constraint across different time periods and economic environments affect the optimal policy responses of central banks and fiscal authorities, along with their implications for macroeconomic outcomes.
Source link
Wejden Ben Jannet www.mdpi.com