1.1.1. Technology Acceptance Model
The TAM illustrates how users adopt and interact with technology based on their perceptions of ease of use and usefulness, which, in turn, influence their attitudes and behavioral intentions [
9]. Given this characteristic, the TAM has been applied in various contexts, including predicting user adoption, improving technology design, and enhancing business strategies [
12,
13,
14]. In particular, the TAM has contributed to advancing knowledge of mobile applications by providing insights into how perceived ease of use and usefulness shape behavioral intentions. For example, Su and colleagues examined how user loyalty toward mobile food delivery applications develops through their experiences with the application and their perceptions of its functionality [
15]. Similarly, in our context, mobile health applications offer various features for monitoring users’ health records and tracking their physical activities. However, there is limited understanding of how users evaluate different features within these applications, how their satisfaction is formed, and how these assessments influence their future behavior. To gain a deeper understanding of users’ evaluations of mobile health applications, it is essential to explore their perceptions of ease of use and usefulness, their satisfaction, and their behavioral intentions through the lens of the TAM.
1.1.2. Perceived Ease of Use and Perceived Usefulness
Perceived ease of use refers to the extent to which individuals perceive that utilizing new technologies or systems requires minimal additional physical or cognitive effort [
16]. Because the perception of ease of use can influence individuals’ adoption and utilization of the application [
17], it is essential to present its functions in a clear and user-friendly manner. Especially since mobile health applications often include various functions that may overwhelm consumers, designing these applications to be user-friendly and for all ages is crucial for business success [
18,
19].
Perceived usefulness is associated with the degree to which individuals believe that using a specific system will lead to better performance in their job role [
20]. Because perceived usefulness can reinforce individuals’ performance, it is acknowledged as a fundamental aspect of technology evaluation. Perceived usefulness has also been shown to exert both direct and indirect influences on attitudes toward technology use, thereby positively shaping the behavioral intention to adopt the technology [
16,
21,
22]. For example, those involved in sport, including athletes and coaches, who acknowledge the value of an electronic competition scoring system are more likely to invest in it [
23]. Therefore, perceived usefulness plays a crucial role in forming consumer attitudes and behaviors.
Furthermore, consumers’ views on the ease of using a product can shape their perception of the application’s overall usefulness. To enhance their perception of usefulness, it is crucial that applications are designed to ensure that their various features are readily accessible. For example, Schnall et al. found that the perceived ease of use of mobile health applications can positively influence users’ perception of the application [
18]. Given this consideration, when users perceive the ease of use of mobile health applications, they are likely to recognize the usefulness of the application.
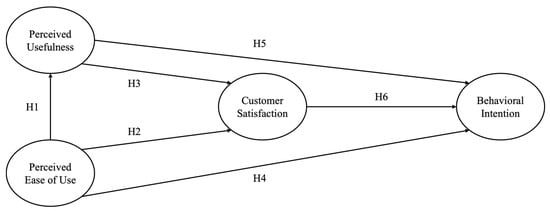
H1. Individuals’ perceived ease of use of mobile health applications will positively influence their perceived usefulness.
1.1.3. Consumer Satisfaction and Acceptance Intention
Customer satisfaction is a subjective evaluation or state of mind centered on the experience of goods, such as tangible and intangible goods as well as information [
24]. It reflects a psychological response based on specific experiences and expectations [
24]. Within the field of consumer behavior, researchers have extensively investigated predictors of consumer satisfaction across various contexts [
25]. For example, fostering consumer satisfaction involves addressing their hedonic and utilitarian needs through social media applications [
26]. For consumers to feel satisfied with using the applications, it is necessary to effectively represent the applications’ characteristics. However, previous research on mobile health applications has primarily focused on how their functionalities influence users’ overall evaluation of the applications and their behavioral intention to use them [
27]. Because the evaluation of a specific brand is formed when consumers use the brand and experience satisfaction, it is essential to understand how individuals’ perceptions of ease of use and usefulness in mobile health applications influence their satisfaction with the applications.
H2. Individuals’ perceived ease of use of mobile health applications will positively influence their satisfaction with the applications.
H3. Individuals’ perceived usefulness of mobile health applications will positively influence their satisfaction with the applications.
Behavioral intention refers to consumers’ willingness or intention to continue adopting a particular product or service [
28]. Because individuals’ behavioral intention is considered a precursor to actual use, it is important to understand how they respond to and engage with a product or service [
28]. To emphasize the importance of behavioral intention, numerous studies have identified various predictors of behavioral intention, which are often used as a key outcome variable and highlighted as a critical factor in decision-making [
29,
30]. In this way, consumers’ behavioral intention to use a product or service is a significant factor in evaluating its functions and shaping their attitudes toward the product or service.
Several studies on mobile applications have highlighted that technological experience, usefulness, and attitudes are important in encouraging individuals’ behavioral intention [
31,
32]. For example, when individuals recognize the valuable advantages of the application, they want to use them in the future [
31]. When users find an application intuitive and effortless to navigate, they are more likely to engage with it consistently and develop a positive attitude toward its use [
12]. Users’ behavioral intentions are strengthened when they receive useful information from the application and positively evaluate their satisfaction with it [
15]. Similarly, when mobile health applications are designed to be easy to use and provide valuable information, they encourage user engagement, foster positive experiences, and enhance perceived utility. As these experiences accumulate, consumers will assess whether to continue using the applications (See
Figure 1).
H4. Individuals’ perceived ease of use of mobile health applications will positively influence their behavioral intention of the applications.
H5. Individuals’ perceived usefulness of mobile health applications will positively influence their behavioral intention of the applications.
H6. Individuals’ satisfaction with mobile health applications will positively influence their behavioral intention of the applications.