This story is part of the Grist arts and culture series Moral Hazards, a weeklong exploration of the complex — sometimes contradictory — factors that drive our ethical decision-making in the age of global warming.
In May 2014, Kate Schapira carted a little table with a hand-painted sign out to a park near her home in Providence, Rhode Island, and started listening to strangers’ problems. The sign read “Climate Anxiety Counseling Booth,” referencing an emotion that was relatively unknown, or at least seldom named, at the time. As an English professor, she had no psychological training, no climate science background. She could not offer expertise, simply an ear and a venue for people to unload worries.
And people came, tentatively but earnestly, as she brought the table out roughly 30 times over the rest of the summer. Those who approached unloaded a variety of concerns — some directly related to climate change, all compounded by it. A man divulged his guilt over not being able to pay for air conditioning to keep his disabled son comfortable at home. A young woman complained that her roommate used so many plastic bottles “she had her own gyre in the ocean,” referring to the Great Pacific Garbage Patch. A former student described his fear of a future in which “everything’s melted and burnt.”
Schapira never intended the booth to be a permanent fixture in her life; she did it the first time, she explains now, as a way to lift herself out of a fog — to hear and be heard. Because everything she read about climate change had made her feel depressed and desperate. And worse, when she attempted to talk to friends and colleagues and loved ones about it, they mostly suggested she was overreacting.
It was also a way to right a wrong, she says now, one for which she felt substantial guilt. Around 2013, a friend with whom Schapira exchanged letters had started to express more and more distress over the cascading evidence of climate change, and her helplessness in the face of it. Schapira felt herself growing increasingly depressed and anxious by her friend’s concerns, and wrote back to assert what we might call, in contemporary therapy parlance, a boundary: “I can’t hear about this anymore.”
“I did someone wrong by saying, ‘I don’t have a place for this for you — there’s no place for this feeling,’” she said. “And then I was like, ‘No, there has to be a place for this feeling.’” (Schapira apologized to her friend for “rejecting an opportunity to listen,” and they continued to talk.)
Schapira ended up spending the next 10 years — minus a couple during the chaos of the COVID-19 pandemic — hauling her booth around New England and the mid-Atlantic. Over time, Schapira observed a pattern to the worries she took in — namely, that the ways in which our world is changing puts a strain on us and our relationships. It dictates how we feel, and then those feelings dictate how we behave. “Whatever the name for that is, I see it in everybody who talks to me,” she said.
By 2019, Schapira noticed that those who approached her counseling booth no longer discussed climate change as a future phenomenon, a problem for grandchildren. It was real, it was present, and they were worried about it now. Many of them were afraid of what they would lose, she said. Something had shifted, and climate anxiety had become a mainstream experience.
Courtesty of Kate Schapira / Lara Henderson
In the information age, awareness spreads very, very fast. In the past 15 or so years, climate change has gone from a niche issue within environmental circles to a widespread public concern. The rise in awareness could be due to any number of factors: decades of grassroots organizing that has pushed major politicians to address carbon emissions; savvier communications from environmental groups and scientists; or the exponential platform growth that youth climate activists like Greta Thunberg found with social media.
But perhaps the simplest and most obvious reason is that extreme weather patterns due to climate change have become impossible to ignore. Or rather, they’ve become impossible to ignore for the rich. Hurricane Sandy brought death to the Hamptons. Much of Miami’s priciest oceanfront property will be partially submerged by the middle of the century. The Woolsey Fire burned down Miley Cyrus’ Malibu mansion. Drake’s Toronto home flooded spectacularly in a supercell storm this summer. (The ocher floodwaters, he observed, looked like an espresso martini.)
It’s easy to disparage the uber-wealthy for the insulation they enjoy from many of life’s challenges. But the more uncomfortable reality is that until quite recently, the same could be said for the average American relative to other people around the world, especially in the Global South. That, too, is no longer the case.
Our planet is transforming in a way that will make life much harder for most people. It already has brought suffering to millions and millions of people. And in the United States, most of us are learning about the scale and significance of this crisis at a point when there is not a whole lot of time to shift course. That realization carries both a mental toll and an emotional reckoning.
The mainstreaming of therapy culture, the explosion of the self-care industrial complex, and the isolation of the COVID-19 pandemic have all laid the groundwork for a very self-focused, individualistic framework for understanding our place on an altered planet. Is it ethical to focus on ourselves and our feelings, when the real harms of climate change are very much upon people with no time to worry about it?
In 2019, Rebecca Weston, co-president of the Climate Psychology Alliance, was invited to a summit to address what climate change would bring to Montana, where she lived at the time. The conference brought together experts with different skill sets, and as a mental health professional, it was the first time she had thought about the emotional toll that climate change would have on communities, mostly around displacement from one’s home. There had been massive flooding in the state that year, followed by wildfires that turned the sky red and poured ash onto neighborhoods.
A few years later, right around the start of the pandemic, Weston began seeing references to “climate anxiety” everywhere. You couldn’t open a newsfeed without seeing a reference to an epidemic of mental health crises about climate change.
“It was in the very typical way that the media frames a particular kind of phenomenon as very white, very upper-middle class, very consumerist-oriented and individualist-oriented,” said Weston, highlighting one New York Times article in particular that she found “deeply offensive.” “And so when we think about climate anxiety, that’s the stereotype that emerges, and it’s a real problem. Because not only do I think that’s real and valid for the person [who experiences it], and she needs empathy, but it also really misidentifies a whole host of experiences that people feel.”
That host of experiences encompasses both existential fear and acute trauma. Can we say that a mother in suburban Illinois stuck in a cycle of consuming news about climate catastrophe is having the same emotional response to climate change as a Yup’ik resident of the Alaskan village of Newtok, which is slowly relocating as chunks of its land are sucked into the Bering Sea? Probably not — the difference is an anticipatory fear of what could be lost versus mourning what already has been lost. That distinction, of course, is defined by privilege.
The backlash to climate anxiety didn’t take long to emerge. In early 2019, the writer Mary Annaïse Heglar published a famous essay that chided white climate activists who deemed climate change “the first existential threat,” failing to recognize that communities of color have always had to reckon with threats to their safety and survival in a racist society.
Jade Sasser, a professor of gender studies and sexuality at the University of California, Riverside, has spent the past five years interviewing predominantly young climate activists of color about their perceptions of the future, specifically with regard to having children. She found that most did not identify with the concept of climate anxiety. It was more: “Climate change makes me feel overwhelmed when I consider it in the context of everything else I’m already grappling with.”
“A lot of the dominant narrative around climate anxiety assumes that people who experience it don’t have other serious pressing anxieties,” she said. “That’s what, I think, leads to it being perceived as a privileged narrative that some people really want to reject.”

Chip Somodevilla / Getty Images
In April 2020, Sarah Jaquette Ray — a professor at California State Polytechnic University, Humboldt — published A Field Guide to Climate Anxiety, an amalgamation of research and actionable advice largely directed toward young people overwhelmed by their fear of a warming future. But over the course of writing and then promoting her book, Ray encountered pushback, largely from young people of color.
One Chicana student referenced offhand, in a class presentation, “the white fragility of worrying about the future,” an observation that hit Ray like a “bolt of lightning.” At a talk Ray gave in South Africa to University of Cape Town students about her book, her discussion of the mental health impacts of confronting climate change was met with dismissal, even indignation: This is just not an issue for my community. We are dealing with drought, starvation, disease, much bigger things than what you are talking about.
“And I remember feeling embarrassed — that I was talking about something like climate anxiety when they were dealing with [issues of] survival,” she said. In 2021, Ray wrote an essay of her own exploring the “overwhelmingly white phenomenon of climate anxiety” for the magazine Scientific American.
AA number of climate psychologists and activists have expressed that the rise of climate anxiety is a normal, even logical reaction to a global existential threat. It’s entirely reasonable to feel worried or sad or enraged about the degradation of ecosystems that have supported human life for eons, especially when humans’ economic progress and development is directly responsible for that degradation.
Which leads to the question: How should we deal with feeling anxious and depressed about climate change? Worrying about the effects of too much carbon in the atmosphere is not an illness to be cured by medical treatment or antidepressants, but it does influence how we behave, which is a key element of climate action.
The field of psychology tells us that human brains try to protect themselves from emotions that hurt us, leading to disengagement and retreat. Psychoanalysis goes a step further, arguing that much of our behavior is dictated by unconscious emotions buried deep within — and to change that behavior, we need to unearth those feelings and deal with them. In 1972, the psychoanalyst Howard Searles wrote that our unconscious psychological defense against anxieties around ecosystem deterioration contributed to a sort of paralysis of action, which was culturally perceived as apathy.
“If we don’t go deeply into those feelings, we become really scared of them, and we then make it much, much harder to stay engaged with the problem,” said Weston, with the Climate Psychology Alliance. She also said that unexamined emotions can lead to burnout: “If [you move] too fast from those feelings to action, it’s not actually processed feelings — it’s push them away, push them away — and invariably that model burns out.”
The premise of the Climate Café, an international initiative to engage people to share their emotions about climate change, originated in the United Kingdom in 2015 and started gaining traction virtually during the pandemic. It’s a gathering where people can simply talk “without feeling pressure to find solutions or take action.”
Weston, as a clinician, has run several of the events, and she describes them taking a “pretty predictable arc”: tentative quiet, followed by a brave participant’s admission of guilt for the future their children would inherit. Then someone else chimes in to express helplessness, or overwhelm, or fear. And then another person gets so uncomfortable with naming those feelings that they interrupt to suggest a petition to sign, and someone else recommends an organization to get involved with. “And immediately,” Weston said, “those feelings are lost,” meaning they’ve been pushed back down and left unprocessed.
A new book edited by the psychotherapist Steffi Bednarek, called Climate, Psychology, and Change, includes a chapter that addresses the question of whether Climate Cafés are “a function of privilege.” The answer the authors arrive at is, essentially, that ignoring or pushing aside feelings of distress about climate change risks “the creation of a fortress mindset and prevents those in the Global North from taking action that is needed.” In other words, people shut down to protect themselves.
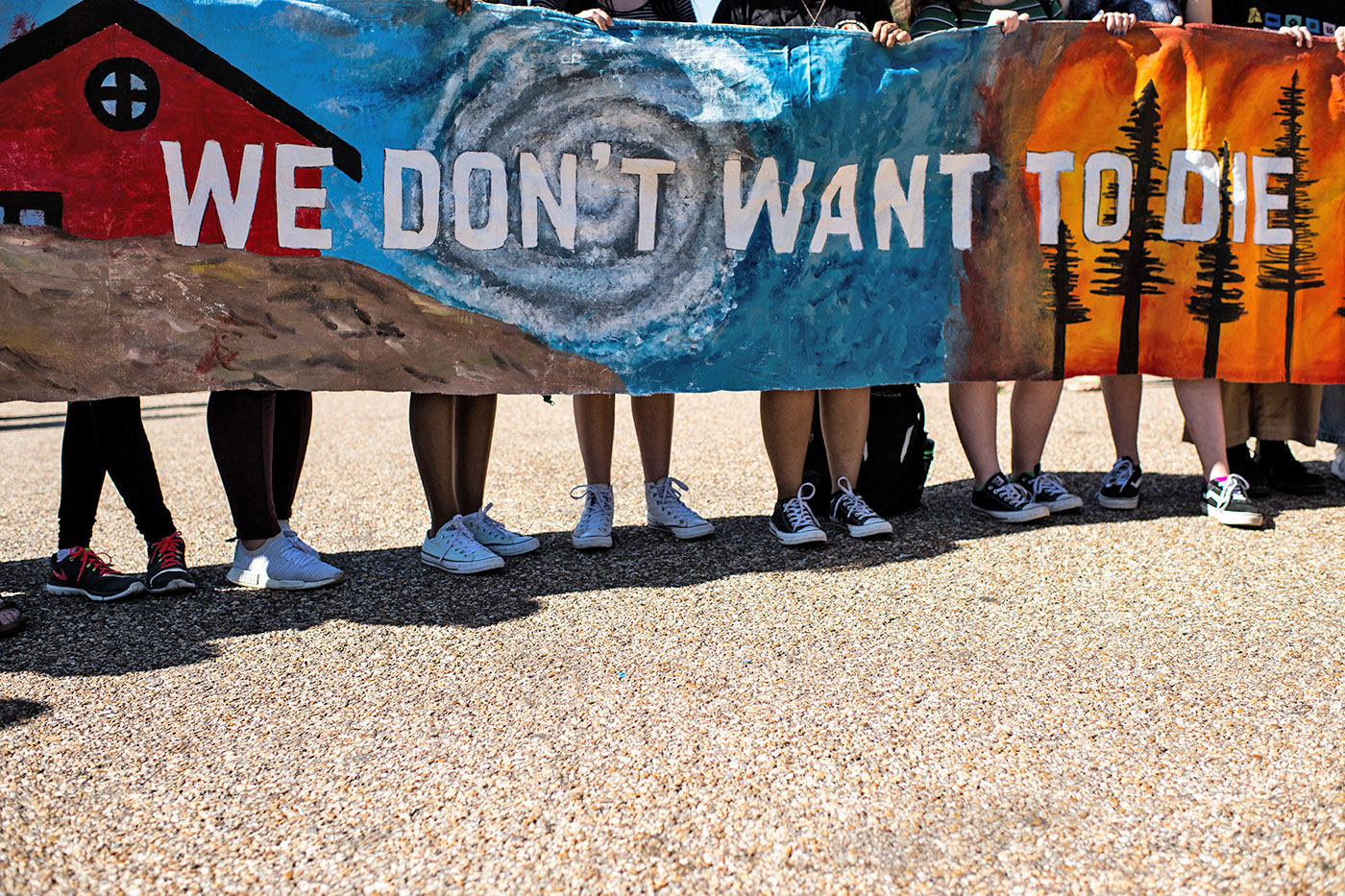
Eric Baradat / AFP via Getty Images
Sasser, in her research with young climate activists of color, encountered a lot of rejection of the idea that we need to process our feelings about the climate crisis. “The rationale was, we don’t have time to sit around feeling sad and worried about climate change because we have to do the work,” she said. “For so many members of marginalized communities, paralysis is not an option. If you’re paralyzed to the point of not taking action to fight for the conditions that you require for survival, then you won’t survive, right?” That’s compounded, she added, by the fact that marginalized communities face many barriers to mental health care.
Then there is the question of whether feelings drive action at all. When climate anxiety became a mainstream concept around 2019, the neuroscientist Kris de Meyer remembered “having debates with people from the therapeutic side, who said that everyone had to go through that emotional quagmire to come out in a place where they could act.” But he argues that it’s the other way around: that emotions are much more predictably the consequence of an action than the driver of one.
His research shows that the complexity of individual response to emotions means that you cannot reliably expect someone to take up arms against fossil fuel companies when they feel fear or rage or despair about climate change. What you can expect is that once that person exercises some sort of action, they’ll lose that feeling of powerlessness.
Another critique of the mental health profession, articulated in Bednarek’s book, is that it has been too shaped by the “capitalist values of individualism, materialism, anthropocentrism, and progress,” with little focus on our collective well-being.
To that end, after a decade of running the climate anxiety booth, Schapira observed that what people expressed to her wasn’t necessarily climate anxiety, but a sense of unease and powerlessness that undergirded all their troubles. That they were so small in the face of massive political, societal, and ecological dysfunction, and had no sense of what they could do to make any of it better.
“Mental health and mental illness themselves are community questions,” she said. “How does a community take care of someone who is in profound distress, but how do communities and societies also create distress? And then, what is their responsibility in addressing and alleviating that distress, even if that distress appears to be internal?”
People told her they began to feel better, she said, when they got involved with something — a group, a campaign, a movement — and found their place as part of something bigger.
In 2018, during Nikayla Jefferson’s last year of undergrad at the University of California, San Diego, she became deeply involved with the youth climate group Sunrise Movement as an organizer. She participated in a hunger strike at the White House. She helped lead the 266-mile protest march from Paradise, California, to Representative Nancy Pelosi’s office in San Francisco to demand stronger federal climate legislation. She published op-eds in national outlets demanding action on a Green New Deal and mobilizing voters for candidates who she felt really understood the gravity of the climate crisis.
Jefferson felt extremely anxious about climate change, but she also felt that that was the “fuel of her climate work” — a special pill she could take to push herself to the extremes of productivity. She had internalized popular messaging of that era of climate activism, specifically that there were 12 years left to stop catastrophic climate change, according to an IPCC projection of a need to curb emissions drastically by the year 2030. “And if we didn’t do this thing, then the world was going to end, and we would fall over some time horizon cliff, and [the Earth] would be completely inhabitable in my lifetime.”
By the end of 2020, she was in the hospital with a debilitating panic attack, and something had to change. She started a meditation practice, got involved in the Buddhist community, and ended her involvement with the Sunrise Movement.
I asked Jefferson about how fellow activists in her generation had related to the idea of climate anxiety, as it was clearly pervasive among its members. There was resistance to using the term, she said, for fear that it would alienate marginalized communities that were important to the movement’s success.
“But I don’t think I agree,” she said. “I think we are all human beings, and we are all experiencing this pretty catastrophic crisis together. And yes, we are all going to be anxious about the future. And if we’re not feeling anxiety about the future, either we have made great strides in our journey of climate acceptance, or we’re in denial.”
Source link
Eve Andrews grist.org





