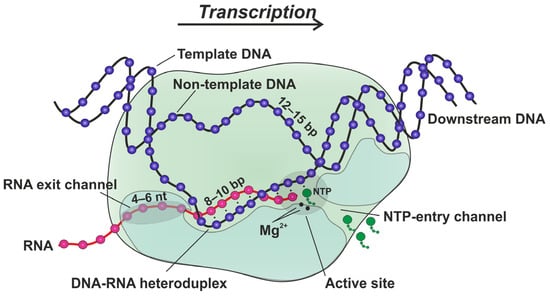
4.2. Enzyme Purification
Briefly, RNAP was isolated from E. coli BL21(DE3) cells transformed with plasmid pVS10 carrying a relevant N-terminal His-tagged gene construct. To purify the enzyme expressed as recombinant proteins, 2 L of culture (in LB broth) of E. coli cells carrying the encoding vector construct was grown with 100 µg/mL ampicillin at 37 °C until A600 reached 0.5–0.7; the expression of the enzyme was induced during 3 h at 37 °C with 1 mM isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside. The cells were harvested by centrifugation (4000 RPM, 20 min at 4 °C) in a Drawell GL-22MC centrifuge (Drawell, Chongqing, China), and the cell pellets were stored at −20 °C. Before proceeding with protein purification, the cell pellets were thawed on ice and resuspended in 30 mL of cell lysis buffer, 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.9), 233 mM NaCl, 2 mM EDTA, 5% glycerol, 0.2% Tween-20, 1 mM β-mercaptoethanol, and a protease inhibitor cocktail (Macklin, Shanghai, China), followed by cell lysis by means of a French press. All the purification procedures were carried out at 4 °C. The homogenate was centrifuged at 15,000 RPM for 15 min. Then, the supernatant was centrifuged under the same conditions. A 5% solution of Polymin P (pH 7.0) was added to the supernatant dropwise to a final concentration of 0.35% with permanent stirring. The obtained suspension was incubated on ice for 15 min and then centrifuged at 15,000 RPM for 15 min. The precipitate was resuspended in 10 mL of buffer 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.9), 300 mM NaCl, 0.1 mM EDTA, 0.1 mM dithiothreitol, and 5% glycerol and then was centrifuged at 15,000 RPM for 15 min. The precipitate was resuspended in 12 mL of buffer 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.9), 1 M NaCl, 0.1 mM EDTA, 0.1 mM dithiothreitol, and 5% glycerol and then was centrifuged under the same conditions. Ammonium sulfate was added to the supernatant to a final concentration of 350 g/L with permanent stirring. The obtained suspension was stirred at 4 °C for 40 min and then was stored on ice overnight. The suspension was centrifuged at 15,000 RPM for 15 min the next day. The precipitate was resuspended in 12 mL of buffer, 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.9), 0.1 mM EDTA, 0.1 mM dithiothreitol, and 5% glycerol and then was centrifuged at 10,000 RPM for 15 min. The supernatant was filtered through a 0.45 um syringe filter (Labfil, Hangzhou, China). The supernatant was diluted twice with a buffer, 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.9), 0.1 mM EDTA, 0.1 mM dithiothreitol, and 5% glycerol and loaded on a 5 mL HiTrap-HeparinTM column (Cytiva GE Healthcare Life Sciences, Marlborough, MA, USA) pre-equilibrated in a buffer, 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.9), and 5% glycerol at a rate of 1 mL/min. The column was washed with 50 mL of a buffer, 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.9), 5% glycerol then with 25 mL of a buffer, 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.9), 450 mM NaCl, and 5% glycerol. The bound proteins were eluted with 25 mL of a buffer, 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.9), 600 mM NaCl, and 5% glycerol. The fraction containing the enzyme was diluted with a buffer, 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.9), and 5% glycerol to a final NaCl concentration of 500 mM and loaded on a 5 mL HiTrap-ChelatingTM column (Cytiva GE Healthcare Life Sciences, Marlborough, MA, USA) pre-equilibrated in a buffer, 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.9) and 500 mM NaCl at a rate of 0.5 mL/min. The column was washed with 5 mL of a buffer, 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.9), and 500 mM NaCl and then with 25 mL of a buffer, 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.9) and 500 mM NaCl, 20 mM imidazole. The bound enzyme was eluted with 25 mL of a buffer, 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.9), 500 mM NaCl, and 200 mM imidazole. The fractions containing RNAP were pooled and dialyzed against 1 L of dialysis buffer, 30 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.9), 50 mM NaCl, 0.5 mM EDTA, 0.1 mM DTT, and 5% glycerol overnight. The dialyzed sample was diluted twice with a buffer, 40 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.9), 1 mM EDTA, 0.1 mM DTT, and 5% glycerol and loaded on a 1 mL Monomix Mab60-Q column (Sepax Technologies, Suzhou, China) pre-equilibrated in the same buffer at a rate of 0.3 mL/min. The column was washed with 5 mL of a buffer, 40 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.9), 1 mM EDTA, 0.1 mM DTT, and 5% glycerol. The bound enzyme was eluted with a 0→600 mM gradient of NaCl. The fractions containing RNAP were pooled and concentrated using a 100,000 MWCO JetSpinTM centrifugal filter (Biofil, Guangzhou, China). Glycerol and DTT were added up to 50% and 1 mM, respectively. The homogeneity of the enzyme was verified by SDS-PAGE; the enzyme concentration was measured using the Bradford method.
4.3. Microscale Thermophoresis (MST)
The stability constant of the transcription elongation complex between the RNAP and R-loop containing the 9 nt bubble was determined by means of a Monolith NT.115 system (NanoTemper Technologies, Yokohama, Japan) using standard capillaries (MonolithTM NT.115 Series, NanoTemper Technologies, Yokohama, Japan).
where fL and fTEC are the specific fluorescence intensities of the free R-loop and the transcription elongation complex TEC; and [L]0 and [E]0 are the total amounts of the R-loop and protein, respectively [21].
4.4. Time Courses of RNA Extension
The reaction was initiated by the rapid mixing of 1 μM TEC (in a buffer, 40 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.9), and 40 mM KCl) with an equal volume of 200 μM NTPs (in a buffer, 20 mM MgCl2, 40 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.9), and 40 mM KCl) at 25 °C. The reaction was quenched at designated intervals by 0.5 M EDTA. EDTA was removed from the samples using Sephadex G-25 (GE Healthcare, Uppsala, Sweden) saturated with 8 M Urea. RNA products were separated in 20% denaturing PAGE, visualized using the VersaDoc Imaging System 4000 MP (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA), and quantified using Gel-Pro40 Analyzer software (Media Cybernetics, Rockville, MD, USA). Two or three individual traces were averaged for each reported curve. The final composition of each reaction mixture was as follows: 0.5 μM RNA primer, 0.55 μM template DNA, 1 μM nontemplate DNA, 1 μM core RNAP, 100 μM NTPs in a reaction buffer, 10 mM MgCl2, 40 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.9), and 40 mM KCl.
Source link
Nadezhda A. Timofeyeva www.mdpi.com