the correlation matrix. In this study, we assume that the pseudo-range measurements at different frequencies share identical random properties, and similarly, the carrier phase observations exhibit consistent random characteristics across frequencies. The STD of the pseudo-range observation is 100 times that of the carrier-phase, i.e.,
. Based on this assumption, combining Formulas (13) and (14), we use the LS method to calculate the variance–covariance matrix of the position parameters
.
is the number of the involved frequencies, ∑ means to sum all elements in the matrix, and
means to take the determinant of the matrix.
, and the same applies below. The matrix
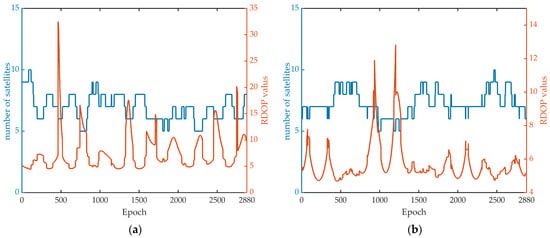
reflects the stochastic characteristics of the estimated position parameters and is a key indicator for evaluating positioning precision.
Source link
Yulu Wang www.mdpi.com