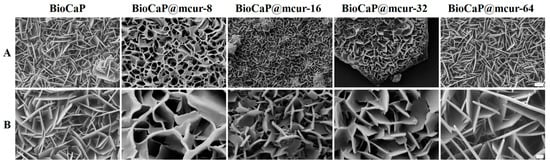
In this study, we fabricated a series of mcur@BioCaP composites mediated by different mcur concentrations through biomimetic mineralization. Flake-like crystals precipitated uniformly on the scaffold surfaces, resulting in a homogeneous calcium phosphate (CaP) coating. Specifically, mcur@BioCaP composites were prepared in the mineralization solutions with mcur concentrations of 8, 16, 32, and 64 µg/mL, designated as mcur@BioCaP-8, mcur@BioCaP-16, mcur@BioCaP-32, and mcur@BioCaP-64, respectively. Subsequent analysis revealed distinct differences in the morphology and micro/nano-structure of the BioCaP coatings, influenced by the presence of mcur (Figure 1A). Notably, mcur@BioCaP exhibited significantly higher surface crystal densities compared to pure BioCaP, likely due to enhanced nucleation and growth facilitated by the organic matrix (mcur) [35,36]. However, the introduction of mcur led to a morphological shift from flake-like to curved structures in the mcur@BioCaP-8, mcur@BioCaP-16, and mcur@BioCaP-32 samples, with an exception noted in the mcur@BioCaP-64 (Figure 1B). Moreover, the size of the crystals in the mcur@BioCaP series was found to be positively correlated with the mcur concentration. This size modulation is ascribed to the amphiphilic nature of mcur, which enables self-assembly into nanoparticles (NPs) at the critical micelle concentration (CMC) [37]. Below a CMC of approximately 65 µg/mL, mcur exists as individual molecules that interact with BioCaP to influence crystal growth and morphology. In contrast, above this CMC, mcur molecules form NPs that do not significantly impact the crystal structure, resulting in plate-like crystals. These findings highlight how the presence of mcur in the biomimetic mineralization process can modify the surface density, size, and morphology of BioCaP crystals without altering their phase. Given the implications of nano/micro-structural properties of CaP particles [38,39,40] on cell toxicity, drug delivery, osteoblast proliferation, and osteoconductivity, the ability to tailor the size of mcur@BioCaP offers valuable opportunities for optimizing bioactivities across various applications. The unique crystal modulation by mcur in the mcur@BioCaP-64 composites is indicative of the potential role of nanoparticle self-assembly in biomimetic mineralization.
Source link
Mingjie Wang www.mdpi.com